SUBCELLULAR COMPONENTS
Introduction
Different organelles constitute the cell. Their analysis by differential centrifugation requires the breaking of the cell’s membrane to release the organelles. They can be separated through a series of centrifugation steps at increasing speed due to their different densities. The membranes are ruptured through a suitable homogenizing medium that burst open the cell. Other methods for cell lysis are by grinding with sand, ultrasonication or the use of high-frequency sound waves, or by enzymatic treatment.
Migration of particles in centrifugation depends on the mass of the particle,
its shape and density and the density of the medium. The three types of
centrifuges are the following: 1.) benchtop- low speed, 4,000-5,000 rpm;
2.) highspeed- maximum at 25,000 rpm, temperature-controlled; 3.) ultracentrifuge-
maximum at 75,000 rpm, kept at low temperature.
Procedure
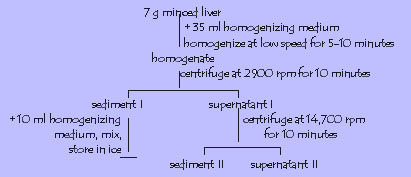
Preparation of tissue: Wash off blood from fresh chicken (or pork, frog, fish) liver using a few drops of the homogenizing medium (0.16 M NaCl or distilled water). Blot with filter paper. Mince. Keep in ice.
Note: Always work at low temperature. Store in ice.

Qualitative test on sediment I, II and supernatant II (with +-control and blank test)
A. Carbohydrates, 1% ribose solution as +-control
2 drops test solution + 2 drops Molisch reagent, shake + 1 ml conc. H2SO4
dropwise or on sides
B. Proteins, 1% albumin solution as +-control
5 drops test solution + 5 drops 10% NaOH + 1 drop 0.5 CuSO4, shake
C. Lipids
5 drops test solution + 1 crystal Sudan IV
D. Nucleic acids, 1% DNA and 1% RNA as +- control
Partial acid hydrolysis: test solutions + 5% 0.1 N HCl, heat for 5-10 min.
a. DNA
1. partially hydrolyzed solution + 5 drops diphenylamine + + 2
drops conc. H2SO4, heat
2. partially hydrolyzed solution + 0.1 N NaOH dropwise until basic + 3 drops Schiff’s reagent, cover and stand for 10 min.
Links :
Back to Main Page
Chemistry 145.1
Human Genome Project and
Bioinformatics
Experiment No. 1
Experiment No. 2
Experiment No. 3
Experiment No. 4
Experiment No. 5
Experiment No. 6
Experiment No. 7
Experiment No. 8
Experiment No. 9
Experiment No.
10
Experiment No.
11
Experiment No.
12
References