
EXPERIMENT NO. 5
EXTRACTION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF PROTEINS
Introduction
Methods to isolate proteins from their natural source by releasing them from the cell include homogenization, by change in osmotic pressure, by high frequency sound waves, by grinding with sand or by treatment with enzymes. Then they are separated from contaminating cellular components by centrifugation, salting out, isoelectric precipitation, or precipitation with organic solvents or acid. Techniques for further purification include column chromatography, density gradient centrifugation, electrophoresis, crystallization and enzymatic digestion.
The two spectrophotometric methods for estimating protein concentration
used in the experiment are the Warburg-Christian and Bradford assays. The
former uses the maximum absorbance of tyrosine and tryptophan residues
at 280 nm for estimating the protein content. Interference caused
by nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids is corrected by measuring absorbance
at 260 nm where the bases absorb strongly. A table is provided for determining
protein purity based on the ratio of the two absorbances. The latter involves
adding Coomasie Brilliant Blue dye to the protein. Under acidic conditions
the binding of the dye to the protein
causes a shift in the wavelength of maximum
absorption for the dye from 465 to 595 nm. Absorbance at 595 nm is related
directly to the protein concentration.
Procedure :
Extraction of proteins :
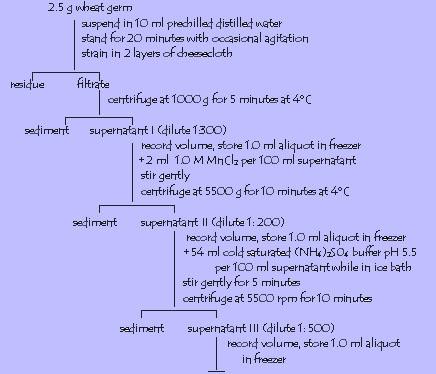
1. Invertase

Activity assay for invertase ( see table on manual for test tube contents)
Maintain the four test tubes in water bath at 37 degrees C for 5-10 minutes. Add 4 ml invertase extract to test tubes 1,3 and 4. Equilibrate for 6 more minutes in water bath. Add 2.0 ml 10% NaOH and Benedictís reagent as test for the presence of reducing sugar.
2. Acid phophatase
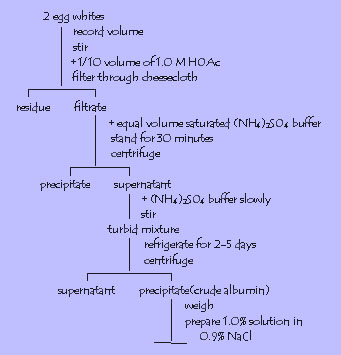
3. Albumin from egg
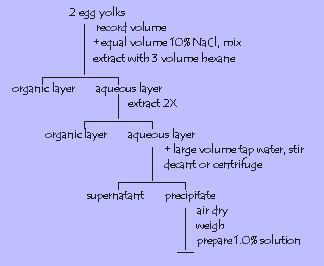
4. Vitellin from egg
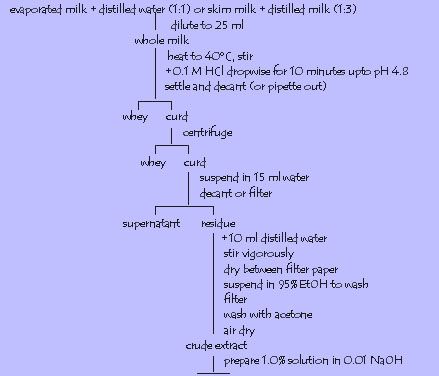
5. Casein from milk
Subsequently perform Warburg-Christian and Bradford assays.
Links :
Back to Main Page
Chemistry 145.1
Human Genome Project and
Bioinformatics
Experiment No. 1
Experiment No. 2
Experiment No. 3
Experiment No. 4
Experiment No. 5
Experiment No. 6
Experiment No. 7
Experiment No. 8
Experiment No. 9
Experiment No.
10
Experiment No.
11
Experiment No.
12
References